VBA Barcode Macro & Functions Tutorial for Microsoft Office 365 Excel, Access & Word on Windows or Mac
IDAutomation VBA Barcode Functions and Macros allow easy generation of barcodes in Microsoft Office 365 Suite applications such as Excel, Word, and Access on both Windows and Mac operating systems, compatible with Excel 2003 and greater in Windows and Excel 2011 and greater on Mac. The VBA modules are also compatible with legacy VB6. These VBA font encoders are used to format data into a special string that will display an accurate barcode when the appropriate font is applied to it; available with any compatible IDAutomation Barcode Font package.
Specific Implementation Tutorials
- Excel 1D for linear barcodes such as Code 128, UPC, and ITF.
- Excel 2D for 2D barcodes such as QR Code, Data Matrix, and PDF417
- Excel Font Encoder VBA App
VBA Barcode Macro & Functions Overview
"The IDAutomation Code 128 Barcode Font and VBA Macros enabled us to integrate barcoding into a Microsoft Excel spreadsheet that works cross-platform between Classic Macintosh, OS X and Microsoft Windows operating systems."
- Charles Daneri, Objective Systems, LLC (computer consulting firm), Baltimore, MD.
These Office Macros consist of pure VBA modules with customizable code, functions, and other options that allow for dynamic and variable data barcode generation. Consequently, this also means that the implementation may be more complicated for the average user. These font encoder tools format data into a text string that will display a readable barcode when the appropriate IDAutomation font is applied to it.
- Import & Export VBA
- Excel Tutorial
- Excel Font Encoder App
- Access Tutorial
- Mail Merge for Word Tutorial
- Barcode Functions
The Macros are free to use with the purchase of any IDAutomation linear barcode font and are compatible with Microsoft Office 2000 and greater running on Windows® or Office 2004 and 2011 for Mac platforms. This tool is not compatible with Office 2008 for Mac because that version does not have VBA capability. IDAutomation has a variety of Mac Barcode Integration options for those using Microsoft Office 2008 for Mac. Mac users and those located outside of the US Western character set should use the IDAutomation Universal Barcode Font Advantage package with related Universal Font VBA functions for Code 128 and Interleaved 2 of 5 fonts.
Importing and Exporting VBA in Excel
The barcode Macros and functions reside inside the Excel file as a custom VBA module. To use these barcode functions in an Excel spreadsheet, the IDAutomationVBA module must be imported. If the IDAutomationVBA.bas file is not available for import, it may be exported from the sample spreadsheet provided in the downloaded file. With all 2D font packages, such as QR-Code and Data-Matrix, the .bas file will reside in the product zip file.
Importing:
- Windows:
- Excel 2010 and above: Add the Developer tab, if it is not already there. Go to File - Options - Customize Ribbon, select Developer under Main Tabs on the right-hand side, and click OK. Now go to Developer - Visual Basic - File - Import File. Step-by-Step Instructions
- Excel 2007: Add the Developer tab, if it is not already there. Right-click on the Office button in the upper left corner of the Excel screen and choose Customize Quick Access Toolbar. Click on Popular at the top of the list on the left, and then click Show Developer Tab in the Ribbon and save. Now go to Developer - Visual Basic - File - Import File
- Excel 1997-2003: Select Tools - Macro - Visual Basic Editor.
- Mac:
- Excel for Mac 2004 and above*: Office
for Mac does not have an import feature in the 2004
version; therefore, users must copy and paste the
necessary RTF file, which is available by request
after purchasing a
Universal Barcode Font license, manually by
going to
Tools - Macros - Visual Basic Editor.
- Once the editor window is open, go to Insert - Module and paste the contents of the RTF file for the corresponding type barcode being used.
- Excel for Mac 2011: Office for Mac has included an import feature in their 2011 version.
Go to
Tools - Macro - Visual Basic Editor.
- Choose the IDAutomation VBA.bas file by right-clicking and selecting Import File. Step-by-Step Instructions
- Excel for Mac 2004 and above*: Office
for Mac does not have an import feature in the 2004
version; therefore, users must copy and paste the
necessary RTF file, which is available by request
after purchasing a
Universal Barcode Font license, manually by
going to
Tools - Macros - Visual Basic Editor.
Very Important: Regardless of the Excel version, after importing the .bas file, immediately save the Excel file as an Excel Macro-Enabled Workbook.
*Note: The Visual Basic Editor feature was removed from Excel for Mac 2008, and thus, this font tool cannot be used in that environment.
Exporting:
- Windows:
- Choose Tools - Macro - Visual Basic Editor.
- Within the editor, choose View - Project Explorer.
- Highlight IDAutomationVBA within the Modules folder and choose File - Export File.
- Name for the exported file: IDAutomationVBA.bas.
Importing and Exporting Macros & VBA in Access
The VBA code, functions, and Macros reside inside the Access database as a VBA module. To use the functions in another Access database, the module must be copied to the other database, or the module must be exported from the sample database and imported into the other database.
- Copy the Module to Another Database: Choose the Modules folder. Highlight the IDAutomationVBA module and choose File - Save As. Save the module to an external file. Choose the database to copy the module to and click OK. This option is not available in all versions of Access.
- Exporting: Choose the Modules folder. Highlight the IDAutomationVBA module and select File - Save As. Save the module to an external file named IDAutomationVBA.
- Importing:
Access 2007 and above: Select the Database Tools tab - Visual Basic.
Choose the Modules folder. Select the IDAutomationVBA file and save the module when asked.
Access 2000 - 2003: Select Tools - Macro - Visual Basic Editor.
Excel VBA Barcode Generation Tutorial
Before starting, ensure that these VBA Macros will achieve the desired goal. If uncertain, consult the Excel Barcode Integration Guide for a variety of scenarios and product suggestions. After downloading the file and extracting its contents, open the sample Excel spreadsheet provided. This spreadsheet contains some examples of various barcode types. A VBA module is included in the sample spreadsheet that contains custom functions and Macros that format data to IDAutomation's barcode fonts. Use the sample spreadsheet as a reference for creating barcodes if help is needed, or contact IDAutomation for additional support.
"I found good documentation on your product, and clearly defined license terms. Your web site is well designed and has a wealth of information. We have been able to implement barcoded data collection and reporting. The barcode font has enabled us to streamline our data collection process significantly. It was extremely simple to set up. We use the Microsoft Excel Macro to create internal forms that can easily be scanned throughout our manufacturing process."
- Thomas Bell, Cynosure, Westford, MA
How to Create a Barcode in Excel
- Enable the security setting that allows Macros to run. If prompted
when the document re-opens, choose
Enable Macros.
- Office 2007 and above applications require the Macros to run from a trusted location.
- Office 2004 and 2011 for Mac settings are located at Excel - Preferences - Security - Macro Security.
- Excel 2000 and 2003 require a medium-security setting to run Macros. Open Excel and set the security level to medium by choosing Tools - Macro - Security.
- Signed Macros are included in the latest
version of the
VBA Module download. Simply choose the
Trust this Publisher option, and the VBA Macros will run unprompted. Data may be pasted into these files and used if the Macros are not modified.
- If a different spreadsheet is used other than the sample
provided, the Macros must be imported
into the spreadsheet.
- Create a column in the spreadsheet for the barcode.
- Size the column to make sure it is wide enough to contain
the entire barcode.
- Format the column so that any text appearing in it will
be centered. This is necessary to create the white space
(often called the quiet zone) before and after the barcode.
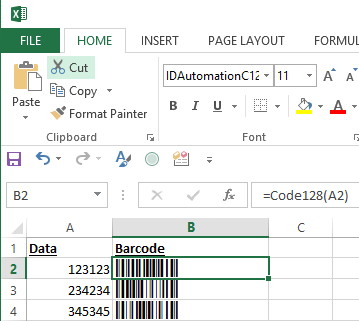
- Enter the formula in this cell that will format the data to the barcode font. If unsure which
function or barcode to use, consider
the
Code 128 barcode fonts with the
=Code128(B10,0) function, where "B10"
refers to the cell location of the data that is to be encoded
and the ",0"
formats the result of the formula to the Code 128 fonts.
For all 2D fonts, refer to the documentation within that
particular package.
- Examine the spreadsheet to make sure the data is being properly formatted to the barcode font. Strange characters may be appended to the beginning and end of the data from the fields, but this is normal. In some cases, the data may need to be reformatted and may appear scrambled. This is normal for Code 128 and Interleaved 2 of 5 barcode fonts when numbers need to be compressed within the barcode.
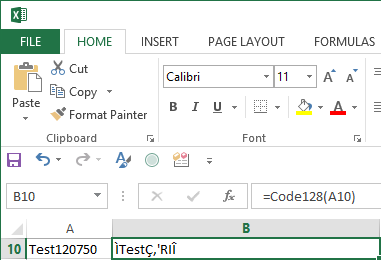
- After verifying that the text in the cell has been formatted
correctly, select the appropriate font and set the point
size to 12. This example selects the
IDAutomationC128XS font. The XS and S sizes of IDAutomation's
fonts in
Code 128 and
Code 39 are specifically designed to format correctly
in Excel, as larger fonts will not usually format correctly
in the cell. 2D symbols within Excel are only possible
with the
2D XLS font for Excel.
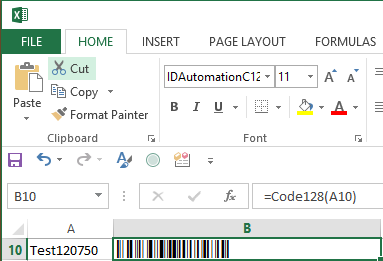
- Ensure that the column is wide enough to contain the
entire barcode with some white space before and after the
barcode.
- Scan the printed barcodes with a handheld USB barcode scanner to verify that the correct data is encoded.
Symbology-Specific Tutorials for Excel:
2D Barcodes:
Linear Barcodes:
- Code 128
- Code 128 for Mac using Universal Fonts
- GS1-128 using Code 128 Fonts
- GS1-128 using the GS1 Fonts
- Interleaved 2 of 5
- GS1 DataBar
- Universal Fonts
- USPS IMb (Intelligent Mail)
- UPC/EAN
Barcoding an Entire Column in Excel
IDAutomation's barcode fonts and Macros provide an easy method of barcoding a column in Excel. In this example, Code 128 barcodes are created in Column B from data in Column A. This example assumes the Code 128 Barcode Font Package has been installed, and the VBA module has been imported into the spreadsheet.
- Enter the formula in one cell to format the data to
the barcode font as explained in the Barcode
Tutorial for Excel:
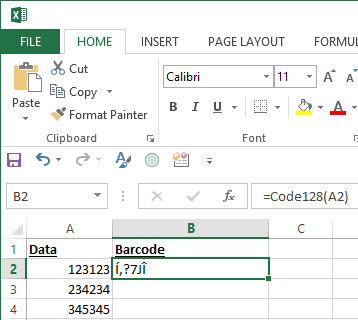
- Select that cell and choose Edit - Copy.
- At this point, it may be necessary to deselect any cells not needed for barcoding. Then, highlight an entire column by selecting the gray square letter-labeled area at the top of the spreadsheet and choose Edit - Paste. In
this example, the button is marked
B. If the spreadsheet is large, the formulas may
take some time to paste and recalculate.
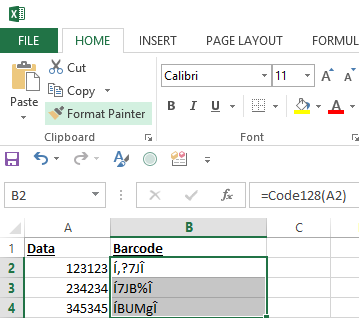
- Change the column to the appropriate barcode font. In
this example, choose the
IDAutomationC128XS font while the entire column that contains the formula is selected. The barcodes will appear in the entire column. When displaying 2D barcodes in Excel, such as QR-Code, Data Matrix, or PDF417, use the
2D XLS Font specifically designed for Excel at 8 points.
- Confirm that the barcodes are accurate by scanning them from printed sheets or directly from the screen. IDAutomation offers a variety of barcode readers that can perform this function with ease.
Video Tutorials
- Video: How to Extract the IDAutomation VBA for Excel
- Video: How to Import the IDAutomation VBA into Excel
- Video: How to Create a Barcode in Excel for Windows
Access VBA Macro Barcode Functions Tutorial
After
the appropriate files have been downloaded and extracted, open
the sample Access database provided. This database contains
one table, one module, and some sample reports. The module contains
custom VBA code, functions, and Macros. The sample database should
be used as a reference if help is needed.
How to Create Barcodes in an Access Report
Before starting this tutorial, ensure that VBA Macros are the desired implementation. Several methods of creating barcodes in Access are explained in the Barcode Integration Guide for Microsoft Access.
- If a different database is being used and not the sample
provided, first import the VBA Macros
into the database.
- The most recent versions of Access require a medium security setting to run Macros.
- Open Access and set the security level to medium by choosing Tools - Macro - Security.
- If prompted when the document is reopened, select
Enable Macros.
Office 2007 and above may require that the Macros run from a trusted location. Signed Macros are included in the latest version of the VBA download. Simply choose the Trust this Publisher option, and the VBA Macros will run unprompted. Tables, Reports, Forms, and other information may be pasted into these files and used if the Macros are not modified.
- Open a report in Design Mode.
- Create a text box where the barcode will display.
- To format the data to the desired barcode font in a
text box, a function must be placed in the Control Source
specifying the data field that needs to be encoded.
- The formula
=function([field]) should be entered
in the Control Source property of the text box, for
example:
=Code128([Serial])
- In some cases, it may be necessary to specify the
table and field in the control source, for example:
=Code128([Table1.Field1])
If unsure of which function to use, consider the =Code128([field]) function with Code 128 Barcode Fonts. - Optional: The Control Source may be changed
to a formula that appends text to the data or combines
multiple fields, for example:
=Code128("PREFIX" & [Field1])or=Code128([Field1] & [Field2])
or=Code128([Field1] & "," & [Field2])
- In Code 128, the
ApplyTilde feature may also be used to encode tab
and return functions. For example, the following formula
creates a tab function between two fields:
=Code128([Field1] & "~009" & [Field2],0,True)
- The formula
=function([field]) should be entered
in the Control Source property of the text box, for
example:
-
 Run
the report to make sure the data is being populated from
the fields and formatted to the barcode font. Strange characters may be appended to the beginning and end of the data, but
this is normal. In some cases, the data may need to be reformatted, and it may appear to be scrambled. This is normal for Code
128, Interleaved 2 of 5, DataBar, and 2D barcodes.
Run
the report to make sure the data is being populated from
the fields and formatted to the barcode font. Strange characters may be appended to the beginning and end of the data, but
this is normal. In some cases, the data may need to be reformatted, and it may appear to be scrambled. This is normal for Code
128, Interleaved 2 of 5, DataBar, and 2D barcodes.
- Change the formula field font to the appropriate barcode font and set the point size to 12. If this step is not followed,
generated barcodes will not display.
- Print and scan the barcodes to verify that the correct data is encoded. If a scanner is needed to verify barcodes, consider the IDAutomation USB Barcode Scanner.
Note: When distributing Access Databases, the associated barcode font must be installed on each computer that prints the barcodes. If this is inconvenient, the Native Barcode Generator for Access is a complete barcode generator object that stays embedded in the database, which means no fonts need to be installed on user computers. For more information about other methods of barcoding in Access, please refer to the Microsoft Access Barcode Integration Guide.
If a large amount of data needs to be encoded, the PDF417 Barcode Font and Encoder or the Data Matrix Barcode Font and Encoder may be the best options, as these 2D barcode types allow for the encoding of more data.
VBA & Macro Functions in Microsoft Word Mail-Merge
Before starting this barcode tutorial, ensure that VBA Macros are the desired implementation for a Word mail merge. An easier method exists when using Codabar or Code 39 fonts, and this is explained further in the Barcode Integration Guide for Microsoft Word.
Excel must be used as the data source when creating barcodes in a Microsoft Word mail merge using Macros. The field used for the data source in Word should be the column in Excel where the formula has been applied, which is used to format the data to the barcode font. It is best to use the last column of the spreadsheet to avoid merging conflicts.
To set up an Excel spreadsheet with these barcode Macros, refer to the Barcode Tutorial for Excel.
Note: C128 ReturnTypes 6 through 9 are not currently supported in Excel-Word mail merges.
- Excel 2000 and 2003 require a medium security setting to run Macros. Open Excel and
set the security level to medium by choosing
Tools - Macro - Security.
Office 2007 and above may require the Macros to run from a trusted location.
In Office 2004 for Mac, go to Excel - Preferences - Security and select Macro Security to enable the secure setting.
- After the files have been downloaded and extracted,
open the included Word Mail-Merge document. A message may
appear stating that the data source cannot be found. If
so, select
Data Source for Word Mail Merge.xls as the data source.
If asked, enable Macros.
- The formula may be viewed in the cells of the
Barcode column in the Excel spreadsheet. This formula
retrieves the data to encode and passes it to the appropriate
barcode function. The function will
then format the data for the barcode font. This column is
then passed to Word when the mail merge is started. The
appropriate barcode font must be selected for the field
in MS Word; in this case, it is
«Barcode».
- The barcode will not look correct and will not scan
until the mail merge is performed.
- After the merge is performed, print and scan the barcode
to verify that the correct data has been encoded. If a scanner
is needed to verify barcodes, IDAutomation suggests easy-to-use
USB Barcode Scanners.
- When distributing the mail merge, the font should be embedded in Word, and the Excel data source must be accessible.
VBA Barcode Macro Functions and Properties
The functions listed below are available in IDAutomation's IDAutomationVBA.bas file and are only valid when used with the font listed in the "font to use" column. Functions beginning with IDAutomation_Uni_ may only be used with the IDAutomation Universal Barcode Font Advantage™ package and are supplied in the IDAutomationWindowsDLLVBA.bas file provided within that package.
DataToEncode is the string data type for all functions listed below. Other data types, such as numbers or dates, may need to be converted to the string data type to be properly encoded. Additional parameters are available for some functions and are optional. For example, Code128("123456",0,True). For UPC-A, UPC-E & EAN-13, the +2 and +5 add-on codes may be created by adding the digits to the end of the data being encoded.
| VBA Functions for Standard Barcode Fonts | |||
| Barcode Type | Barcode Function Methods | Notes | VBA File to Import | Required Font |
| Code-11 | Code11 (DataToEncode) | IDAutomationVBA.bas | IDAutomationC11 |
|
Code-128 (Auto Mode) |
Code128 (DataToEncode,
C128 ReturnType,
ApplyTilde) Human-readable text is enabled when ReturnType = 6 Example: Code128("123456789012", 6, 0) |
IDAutomationVBA.bas or IDAutomation VBA for Code 128 and Postnet.bas* |
IDAutomationC128 |
|
Code-128 (Manual Mode) |
IDAutomation recommends
using Auto Mode for most situations. Code128a (DataToEncode, C128 ReturnType) Code128b (DataToEncode, C128 ReturnType) Code128c (DataToEncode, C128 ReturnType) Example: Code128b("12345678", 6) |
IDAutomationVBA.bas or IDAutomation VBA for Code 128 and Postnet.bas* |
IDAutomationC128 |
| Code-39 |
Code39 (DataToEncode) Code39Mod43 (DataToEncode, ReturnType) Example: Code39Mod43("12345678", 0) |
IDAutomationVBA.bas | IDAutomationC39 |
| Code-93 | Code93 (DataToEncode) | IDAutomationVBA.bas | IDAutomationC93 |
| Codabar | Codabar (DataToEncode) | IDAutomationVBA.bas | IDAutomationCB |
| EAN-13 | IDAEAN13 (DataToEncode) | IDAutomationVBA.bas | IDAutomationUPCEAN |
| EAN-8 | IDAEAN8 (DataToEncode) | IDAutomationVBA.bas | IDAutomationUPCEAN |
| GS1-128 |
Code128 (DataToEncode,
C128 ReturnType,
1) GS1-128 is enabled in Code 128 Auto by setting ApplyTilde to True. Human-readable AIs may be created by setting the C128 ReturnType to 6. Example: Code128("(12)3456789012", 6, 1) |
IDAutomationVBA.bas or IDAutomation VBA for Code 128 and Postnet.bas* |
IDAutomationC128 |
| Interleaved 2 of 5 |
I2of5 (DataToEncode) I2of5Mod10 (DataToEncode, ReturnType) Example: I2of5Mod10("123456789", 1) NOTE: ReturnType 3 generates an OPC (Optical Product Code) symbol. OPC is also known as Vision Council of America OPC, VCA BarCode & VCA OPC. Example: I2of5Mod10("020748721", 3) |
IDAutomationVBA.bas | IDAutomationI25 |
| MSI / Plessey | MSI (DataToEncode, ReturnType) | IDAutomationVBA.bas | IDAutomationMSI |
| RM4SCC | RM4SCC (DataToEncode) | IDAutomationVBA.bas | IDAutomationRM |
| UPC-A | UPCa (DataToEncode) | IDAutomationVBA.bas | IDAutomationUPCEAN |
| UPC-E | UPCe (DataToEncode) | IDAutomationVBA.bas | IDAutomationUPCEAN |
| USPS IntelligentMail (IMb) |
IntelligentMail (DataToEncode)
** Included only in the purchased version of the USPS IMb Font Package. |
IDAutomation VBA for Intelligent Mail.bas |
IDAutomationPOSTNET or IDAutomationIMB |
| USPS Postnet |
Postnet (DataToEncode,
ReturnType) *Included in Postnet package. |
IDAutomationVBA.bas or IDAutomation VBA for Code 128 and Postnet.bas* |
IDAutomationPOSTNET |
| USPS Planet | Planet (DataToEncode, ReturnType) | IDAutomationVBA.bas or IDAutomation VBA for Code 128 and Postnet.bas* |
IDAutomationPOSTNET |
| not applicable | MOD10 (DataToEncode) | IDAutomationVBA.bas | not applicable |
| not applicable | SpliceText (DataToEncode, SpacingNumber, ApplyTilde) | IDAutomationVBA.bas | not applicable |
| Functions for the Universal Barcode Font | |||
|
All functions listed below are preceded by IDAutomation_Uni_.* They may only be used with
the
IDAutomation Universal Barcode Font Advantage™
and are supplied in the
IDAutomation_UniversalFont_VBA.bas or the
IDAutomationWindowsDLLVBA.bas file, which also
requires the installation of the product EXE file for the macro to function because they access
an installed
IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll that is provided
within the package. Note: Excel 2004 for Mac requires the functions to be lowercase. Ex: idautomation_uni_c128 |
|||
| Barcode Type | Universal Function Methods | Notes | VBA File to Import | Required Font |
| Code-128 |
IDAutomation_Uni_C128 (DataToEncode,
ApplyTilde) Note: Code128() is the recommended method to use. Code128() is also used to create GS1-128. IDAutomation_Uni_C128A (DataToEncode) IDAutomation_Uni_C128B (DataToEncode) IDAutomation_Uni_C128C (DataToEncode) Example: IDAutomation_Uni_C128 ("Ê8100712345Ê2112WH5678", TRUE) Excel for Mac: idautomation_uni_c128 ("Ê8100712345Ê2112WH5678", TRUE) |
IDAutomation_UniversalFont_VBA.bas or IDautomation_WindowsDLLVBA.bas and IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll |
IDAutomation_Uni |
| not applicable | C128HR (DataToEncode,
ApplyTilde) Returns text for Code 128 barcodes, such as for GS1-128. |
IDAutomation_UniversalFont_VBA.bas or IDautomation_WindowsDLLVBA.bas and IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll |
Text Font |
| Code-39 |
IDAutomation_Uni_C39 (DataToEncode,
N_Dimension,
IncludeCheckDigit) Example: IDAutomation_Uni_C39 ("123456789", 3, TRUE ) Excel for Mac: idautomation_uni_c39 ("123456789", 3, TRUE ) |
IDAutomation_UniversalFont_VBA.bas or IDautomation_WindowsDLLVBA.bas and IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll |
IDAutomation_Uni |
| Codabar |
IDAutomation_Uni_Codabar (DataToEncode,
N_Dimension, StartChar, StopChar) Example: IDAutomation_Uni_Codabar ("123456789", 3,"A","B" ) Excel for Mac: idautomation_uni_codabar ("123456789", 3,"A","B" ) |
IDAutomation_UniversalFont_VBA.bas or IDautomation_WindowsDLLVBA.bas and IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll |
IDAutomation_Uni |
| Interleaved 2 of 5 | IDAutomation_Uni_I2of5 (DataToEncode, N_Dimension, IncludeCheckDigit) | IDAutomation_UniversalFont_VBA.bas or IDautomation_WindowsDLLVBA.bas and IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll |
IDAutomation_Uni |
| MSI / Plessey | IDAutomation_Uni_MSI (DataToEncode, N_Dimension, IncludeCheckDigit) | IDAutomation_UniversalFont_VBA.bas or IDautomation_WindowsDLLVBA.bas and IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll |
IDAutomation_Uni |
| USPS IntelligentMail | IDAutomation_Uni_IntelligentMail (DataToEncode) ** | IDAutomation_UniversalFont_USPS_IMb_VBA.bas | IDAutomation_Uni |
| USPS Postnet | IDAutomation_Uni_Postnet (DataToEncode, IncludeCheckDigit) |
IDAutomation_UniversalFont_VBA.bas or IDautomation_WindowsDLLVBA.bas and IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll |
IDAutomation_Uni |
| USPS Planet | IDAutomation_Uni_Planet (DataToEncode, IncludeCheckDigit) | IDAutomation_UniversalFont_VBA.bas or IDautomation_WindowsDLLVBA.bas and IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll |
IDAutomation_Uni |
| Functions for the DataBar Barcode Font | |||
| The functions listed below are preceded by IDAutomation_GS1 and are only provided with the IDAutomation DataBar Font Advantage Package. | |||
| Barcode Type | DataBar Barcode Function Methods | Notes | VBA File to Import | Required Font |
| DataBar | DataBar (DataToEncode) | IDAutomationGS1DataBar.bas | IDAutomation DataBar 34 |
| DataBar Expanded | DataBarExpanded (DataToEncode, 22) | IDAutomationGS1DataBar.bas | IDAutomation DataBar 34 |
| DataBar Exp. Stacked | DataBarExpanded (DataToEncode, Segments) | IDAutomationGS1DataBar.bas | IDAutomation DataBar 34 |
| DataBar Stacked Omnidirectional | DataBarStacked (DataToEncode) | IDAutomationGS1DataBar.bas | IDAutomation DataBar 34 |
| The functions listed below are rare and not approved for POS systems. | |||
| DataBar Limited | DataBarLimited (DataToEncode) (Not approved for POS) | IDAutomationNativeWindowsDLLVBA.bas and IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll | IDAutomation DataBar 13 |
| DataBar Stacked | DataBarStacked (DataToEncode) (Not approved for POS) | IDAutomationNativeWindowsDLLVBA.bas and IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll | IDAutomation DataBar 13 |
| DataBar Truncated | DataBar (DataToEncode) (Not approved for POS) | IDAutomationNativeWindowsDLLVBA.bas and IDAutomationNativeFontEncoder.dll | IDAutomation DataBar 13 |
| 2D Font Functions | |||
Regarding all symbologies listed in this section
below:
|
|||
| Barcode Type | 2D Function Methods | Notes | VBA File to Import | Required Font |
| Data Matrix | IDAutomation_DMatrix_FontEncoder(ByVal DataToEncode As String, Optional ApplyTilde As Integer = 1, Optional EncMode As Integer = -1,Optional preferredFormat As Integer = -1, Optional NewLineCharacter As String = vbCrLf) As String Complete VBA is only provided in the purchased version. |
IDAutomation_VBA_DataMatrix_FE2021.bas (2021 Release) |
IDAutomation2D or IDAutomationDMatrix |
| EncNDM(DataToEncode As String, Optional ApplyTilde As Integer = 0, Optional EncodingMode As Integer = 0, Optional preferredFormat As Integer = -1) As String |
IDAutomation_Native_DataMatrix_Mac.rtf |
||
| QR-Code | IDAutomation_QRFontEncoder(DataToEncode) All parameters are set to default except ApplyTilde, which is set to 1. |
IDAutomation_VBA_QRCode_FE2021 (2021 Release) |
IDAutomation2D |
| PDF417 | IDAutomation_PDF417(DataToEncode As String, Optional EccLevel As Integer, Optional ColumnSpecify As Integer, Optional RowSpecify As Integer, Optional Truncate As Integer, Optional ForceBinary As Integer) As String | IDAutomation_Native_PDF417_Macro.bas | IDAutomation2D or IDAutomationPDF417 |
| IDAutomation_PDF417(DataToEncode As String, Optional EcLevel As Integer, Optional TotalColumns As Integer, Optional TotalRows As Integer, Optional Truncated As Integer, Optional PDFMode As Integer, Optional ApplyTilde As Integer) As String |
IDAutomation_PDF417_Macro.bas and IDAutomationPDF417.dll (Legacy ActiveX Version) |
||
| Aztec | EncAztec(DataToEncode
As String, Optional ProcessTilde, Optional Error Correction) |
IDAutomation_Aztec_Macro.bas
and IDAutomationAztec.dll |
IDAutomation2D |
| Maxicode | EncMC(DataToEncode
as String, Optional
EncodingMode as Int) The default Encoding Mode is 2 |
IDAutomation_MaxiCode_Macros.bas | IDAutomation Maxicode |
Barcode Function Descriptions
- ApplyTilde: If set to "1" or "True", characters following the tilde may be used to perform additional calculations or encode ASCII characters directly.
- DataToEncode: This string value represents the data being encoded.
- N_Dimension: Determines the width of the wide bars when applicable, which is a multiple of the X dimension. Valid values are 2, 2.5, and 3. The default is 2. The X dimension is determined by the font point size.
- IncludeCheckDigit: A Boolean value that determines whether a check digit should be automatically calculated and included for the DataToEncode.
- Segments: Reducing segments to a low, even number, such as 4, 6, or 8, in a DataBar Expanded symbol can create a stacked barcode. The default is 22.
** The USPS Intelligent Mail (IMb) function is supplied in pure VBA code with the purchased version of the associated font package.

